MetalFab G2
Core
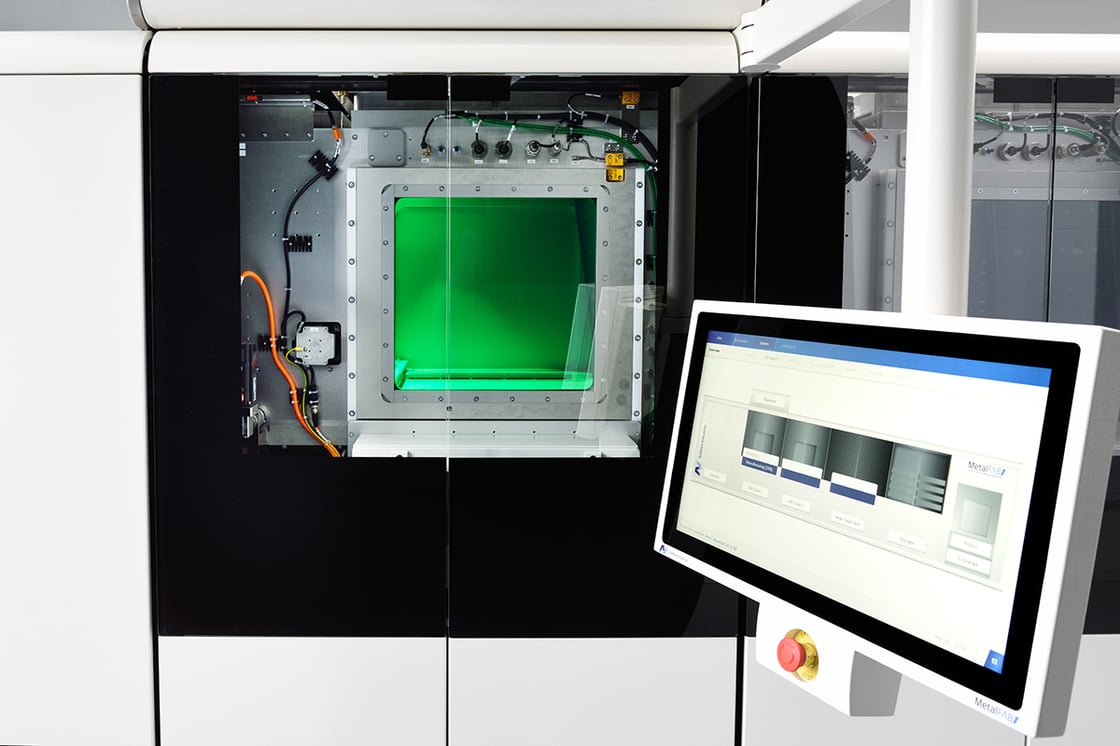
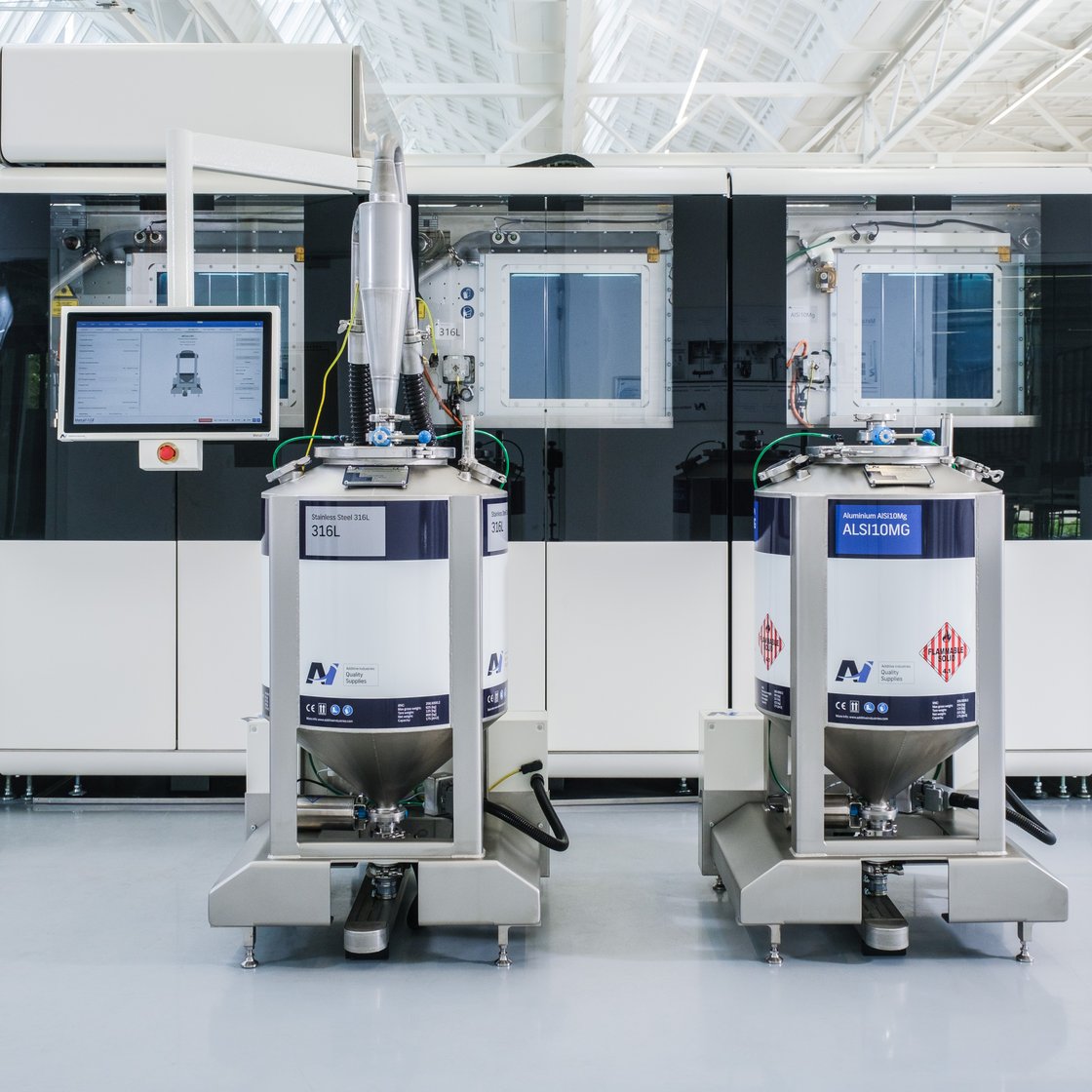
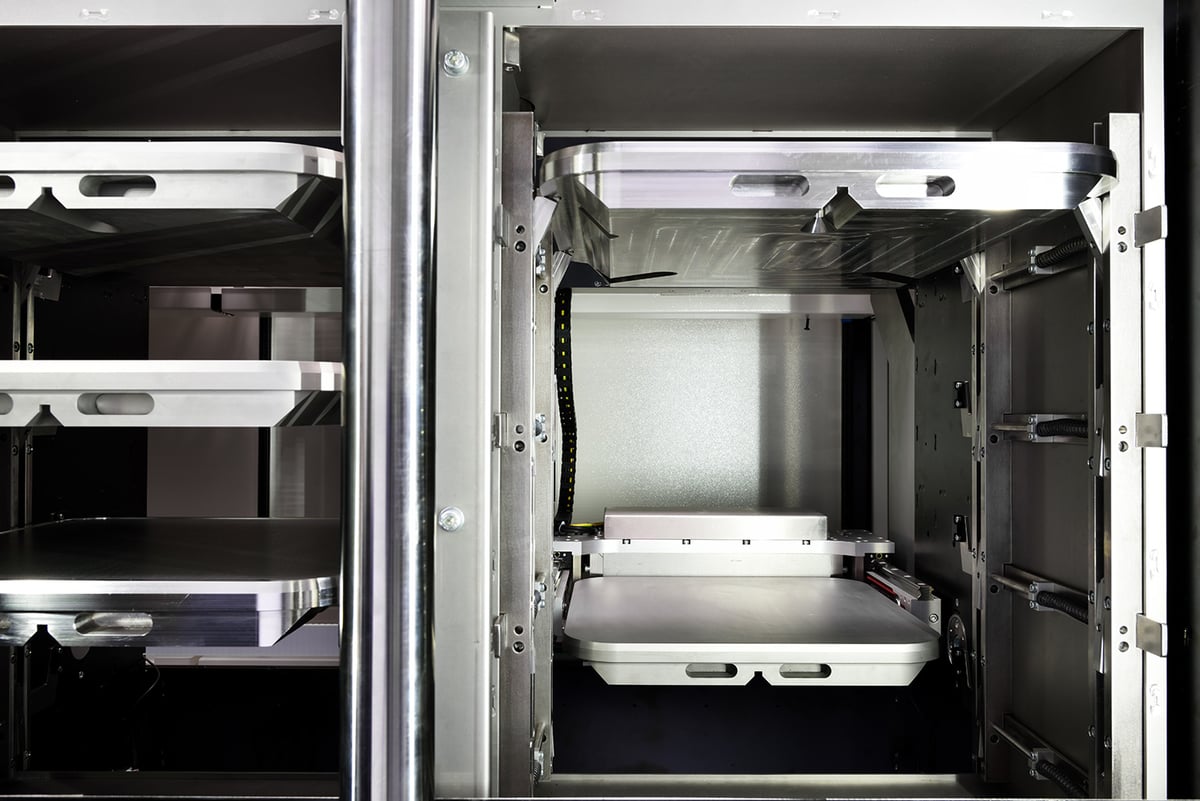
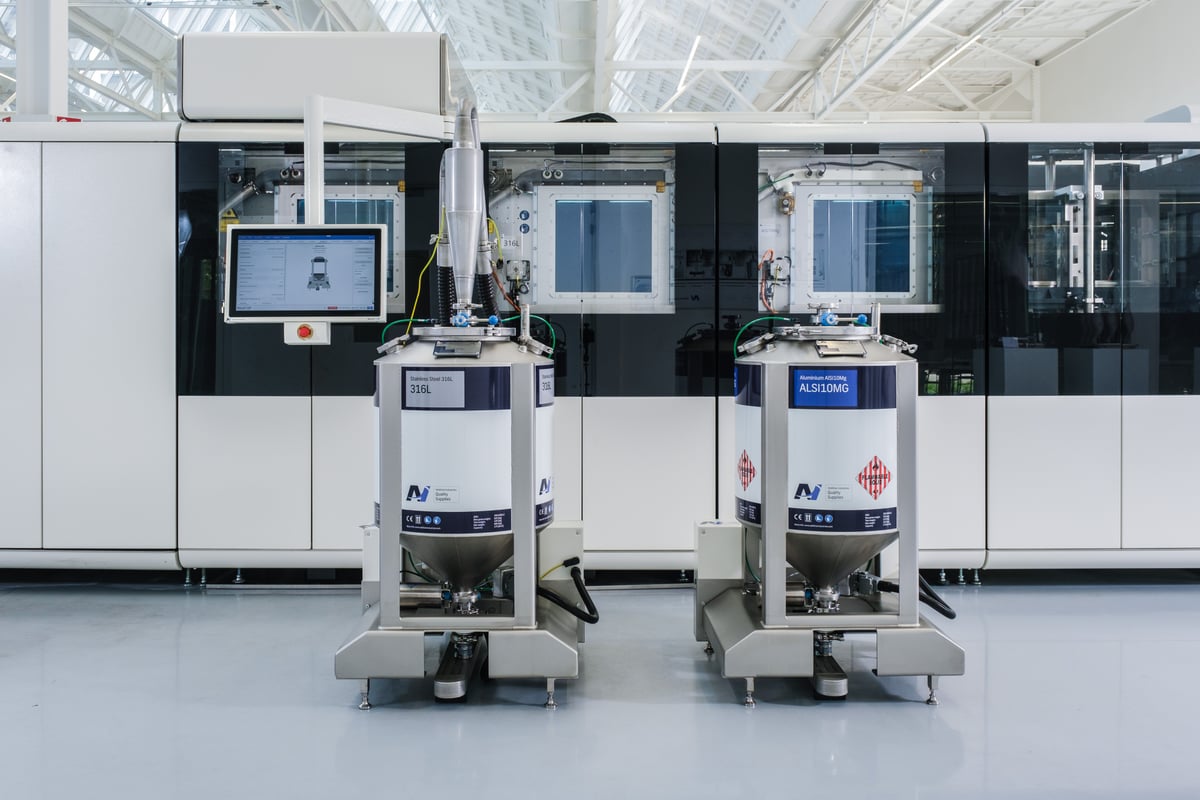
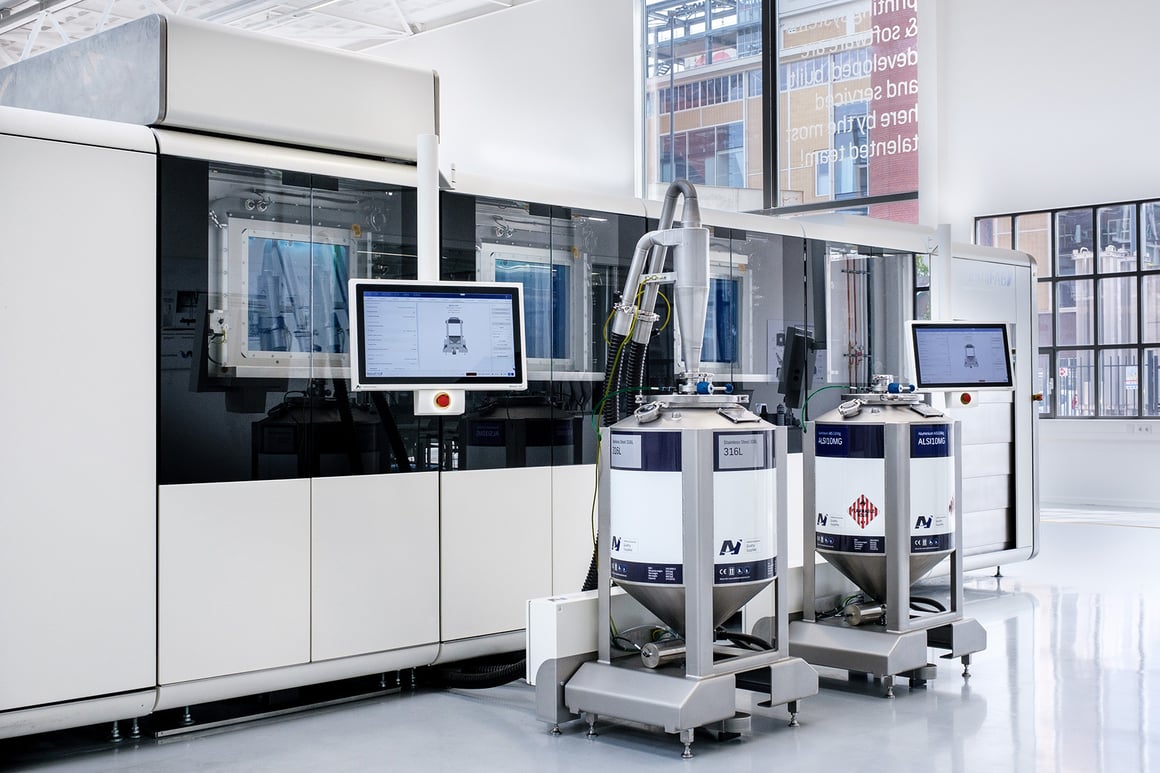
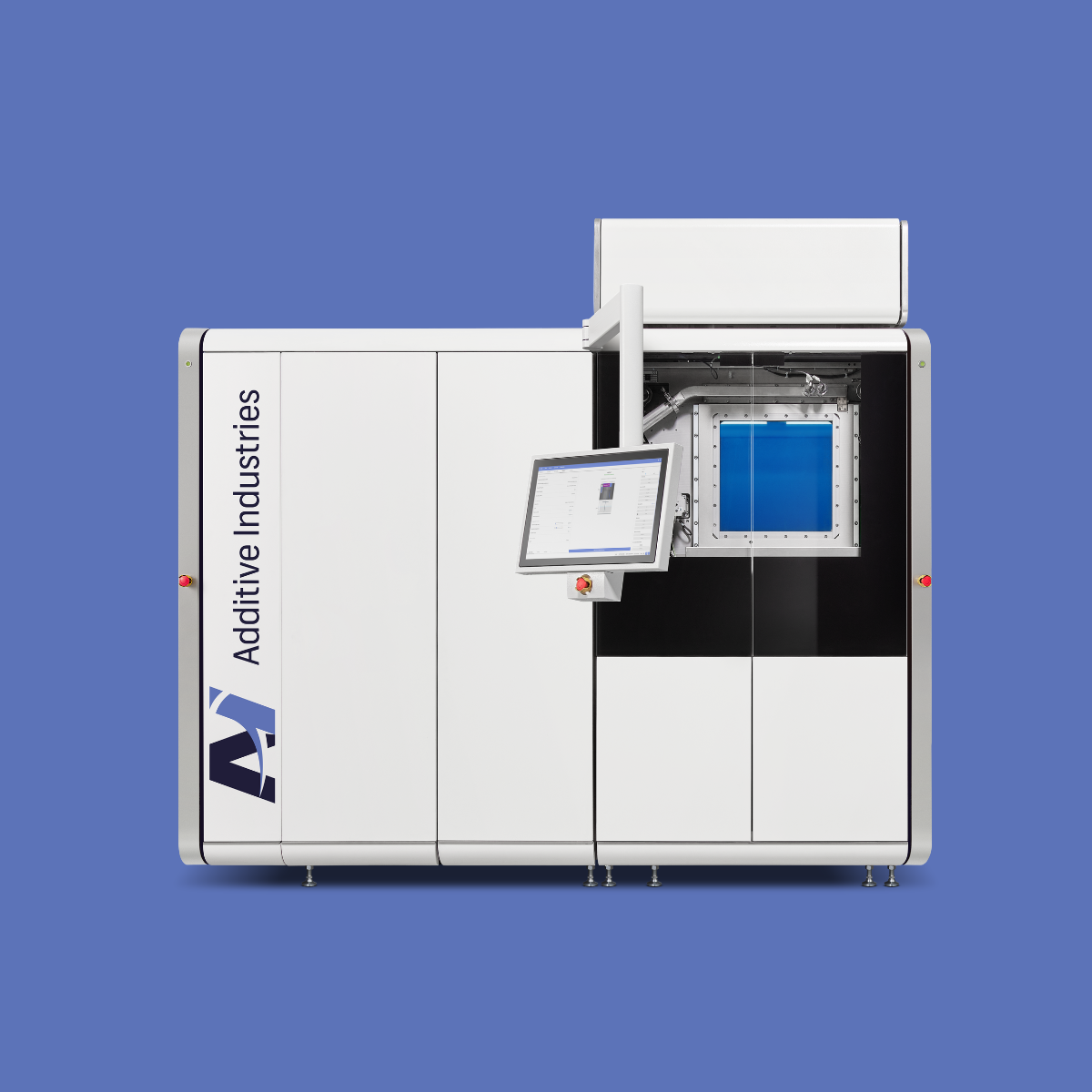
The base system: choose from 1 to 4 x 500W lasers, automated powder extraction, sieving, transportation, laser calibration sequence and base plate levelling for job starts - all come as standard. Build plates are loaded and unloaded from the front of the system manually for job changeover.






.jpg?width=1120&name=bvof-additive-industries-metalfab1-7-hr%20(1).jpg)